can alcohol cause ketoacidosis Ketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria transplantation principles immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious and potentially life-threatening complication of diabetes. It occurs when there is a severe lack of insulin in the body, leading to high blood sugar levels and the production of ketones. Ketones are acidic by-products that accumulate in the blood, causing the body to become acidic. This condition requires immediate medical attention and is commonly seen in individuals with type 1 diabetes.
A Visual Representation of DKA
 One of the best ways to understand DKA is through a visual representation, as shown in the image above. This image highlights the key components of DKA, including high blood sugar levels, the production of ketones, and the potential complications that can arise if not treated promptly.
One of the best ways to understand DKA is through a visual representation, as shown in the image above. This image highlights the key components of DKA, including high blood sugar levels, the production of ketones, and the potential complications that can arise if not treated promptly.
The Role of the Ketogenic Diet
 There has been growing interest in the ketogenic diet as a potential therapeutic approach for managing diabetes and related complications. Although the ketogenic diet, which is high in fat and low in carbohydrates, is primarily known for its use in weight loss, it has shown promising results in improving blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes.
There has been growing interest in the ketogenic diet as a potential therapeutic approach for managing diabetes and related complications. Although the ketogenic diet, which is high in fat and low in carbohydrates, is primarily known for its use in weight loss, it has shown promising results in improving blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes.
Research suggests that a well-formulated ketogenic diet may help regulate blood sugar levels, reduce insulin requirements, and promote weight loss. This is particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes as it can aid in managing their condition and potentially reduce the risk of developing DKA.
The Importance of Medical Supervision
While the ketogenic diet may show promise, it is crucial to note that any dietary changes should be undertaken under the supervision of a healthcare professional. Diabetes management is a complex process, and individualized care is necessary to ensure optimal health outcomes.
A healthcare professional can provide guidance on the appropriate macronutrient distribution, monitor blood sugar levels, and adjust medications accordingly. This collaborative approach between the individual and their healthcare team is essential for achieving and maintaining glycemic control.
Additionally, healthcare professionals can help educate individuals with diabetes about the potential risks and benefits of the ketogenic diet. They can provide valuable information on food selection, portion sizes, and meal planning to ensure a well-balanced and nutrient-dense diet.
Conclusion
Diabetic Ketoacidosis is a severe complication of diabetes that requires immediate medical attention. Understanding the key components of DKA, such as high blood sugar levels and the production of ketones, can help individuals recognize the signs and symptoms.
Although the ketogenic diet may offer potential benefits for individuals with diabetes, it is crucial to approach dietary changes under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Collaborative care and individualized management are essential to achieve optimal health outcomes and reduce the risk of complications like DKA.
If you are searching about Pin on KETO DIET AND INFO you’ve came to the right page. We have 5 Pictures about Pin on KETO DIET AND INFO like Alcoholic Ketoacidosis: Mind the Gap, Give Patients What They Need EMRA, Diabetic Ketoacidosis | EKF Diagnostics - Stanbio and also Pin on KETO DIET AND INFO. Here it is:
Pin On KETO DIET AND INFO
 www.pinterest.comketosis ketoacidosis dka ketogenic lowcarbalpha
www.pinterest.comketosis ketoacidosis dka ketogenic lowcarbalpha
SGLT2 Inhibitor-induced Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Renal Fellow
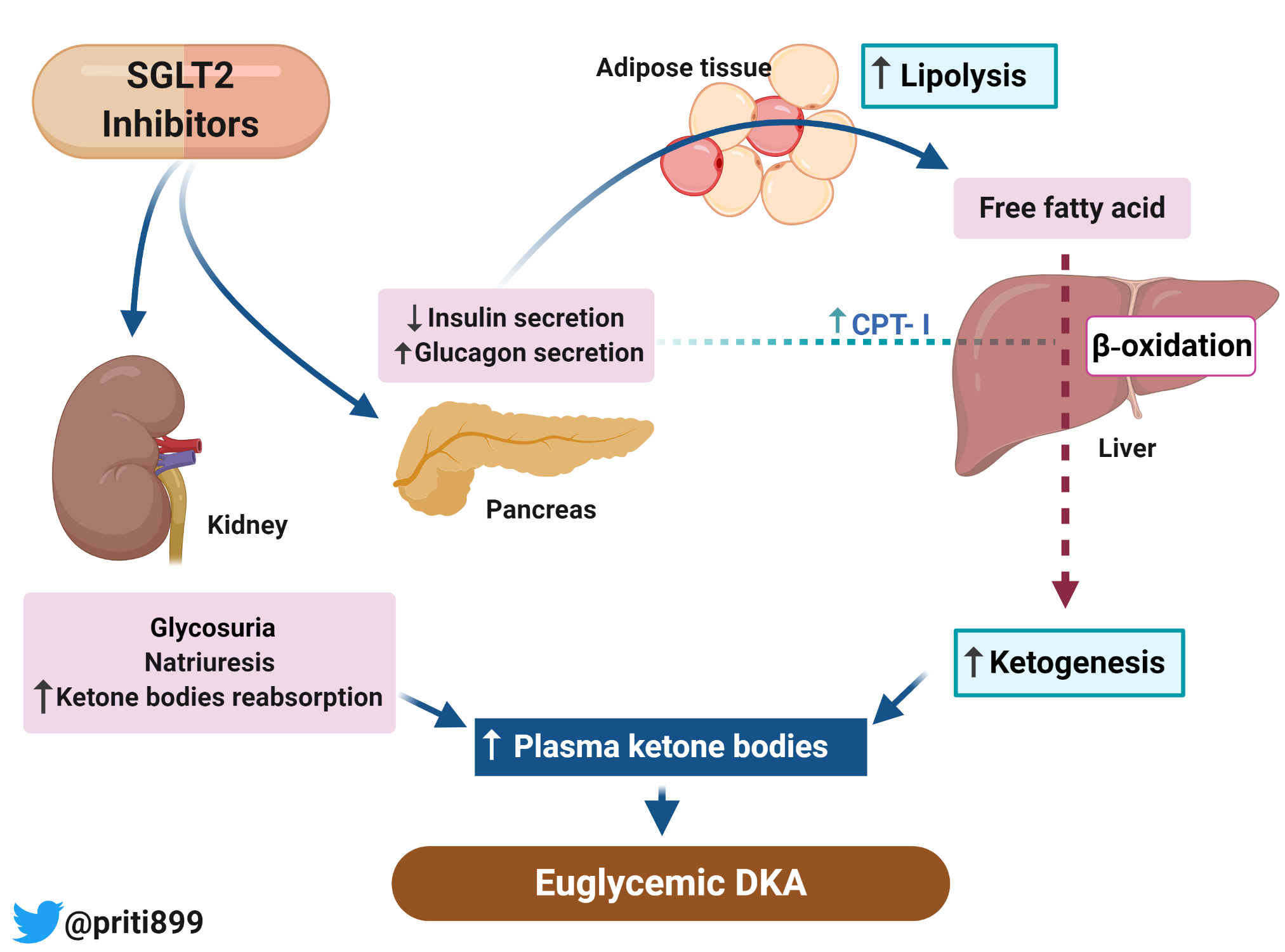 www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria transplantation principles immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
www.renalfellow.orgketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria transplantation principles immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow
Pathogenesis Of Diabetic Ketoacidosis | Download Scientific Diagram
 www.researchgate.netketoacidosis diabetic pathogenesis
www.researchgate.netketoacidosis diabetic pathogenesis
Alcoholic Ketoacidosis: Mind The Gap, Give Patients What They Need EMRA
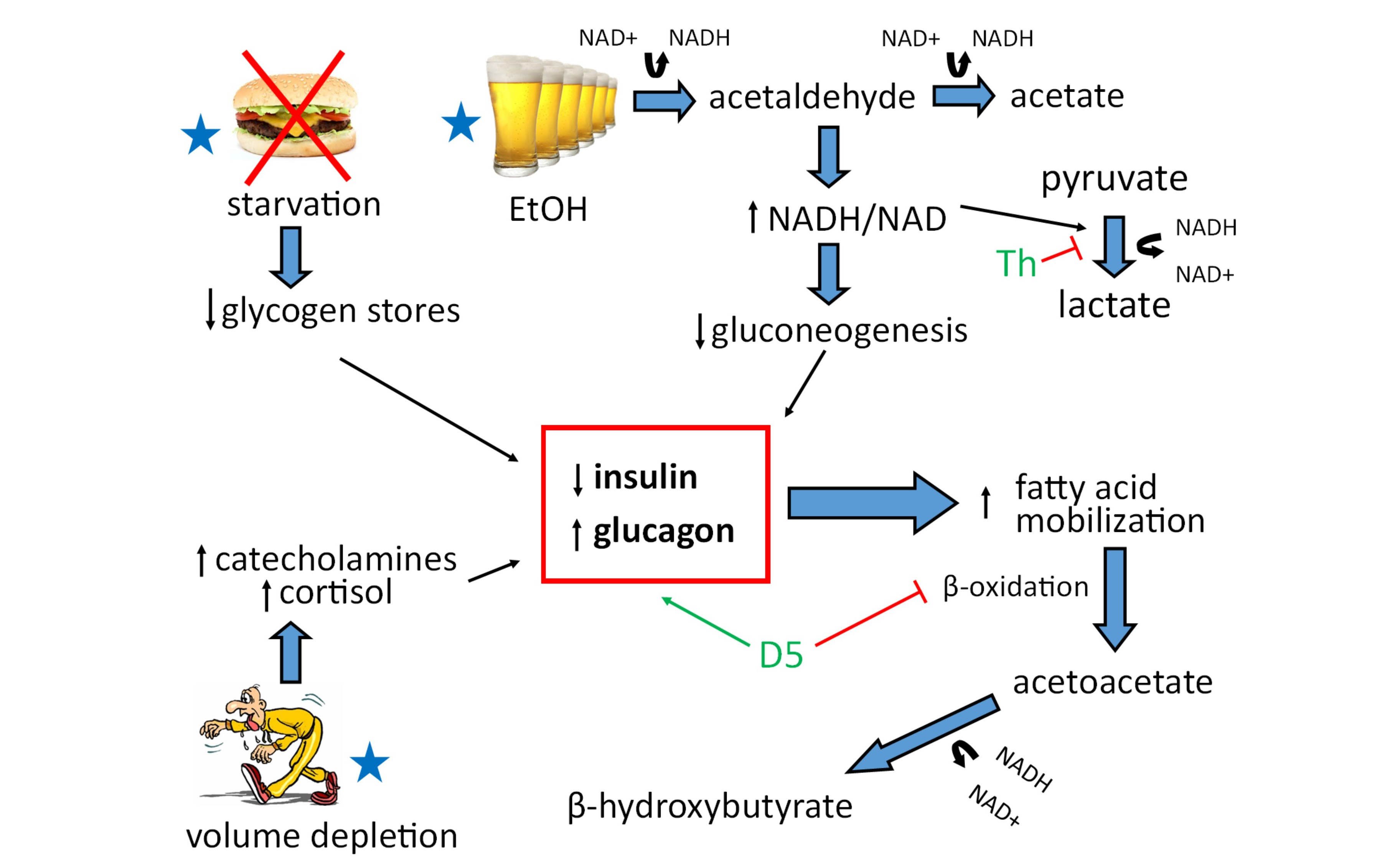 www.emra.orgketoacidosis alcoholic gap alcohol thiamine withdrawal patients popularquotesimg emra
www.emra.orgketoacidosis alcoholic gap alcohol thiamine withdrawal patients popularquotesimg emra
Diabetic Ketoacidosis | EKF Diagnostics - Stanbio
 www.ekfusa.comketoacidosis hydroxybutyrate diabetic beta dka bhb test glucose blood insulin levels why liver illustration cells than
www.ekfusa.comketoacidosis hydroxybutyrate diabetic beta dka bhb test glucose blood insulin levels why liver illustration cells than
Diabetic ketoacidosis. Ketoacidosis sglt2 euglycemic inhibitor induced urine sediment mitochondria transplantation principles immunologic bacterial forms renal renalfellow. Ketoacidosis alcoholic gap alcohol thiamine withdrawal patients popularquotesimg emra